Laparoscopic TVT Mesh Removal and Burch Procedure for the Treatment of Pelvic Pain and Stress Urine Incontinence
This patient is a 46-year-old woman who has had 3 pregnancies and 3 vaginal deliveries and approaches Drs. Miklos and Moore with a chief complaint of urine incontinence and pelvic pain. She admits to urgency, frequency, and nighttime urination. She is not currently sexually active due to painful intercourse ie sex since 2011 when she had her hysterectomy and Sparc TVT mesh sling implanted. She claims the pain is made worse with penile entry and thrusting. (Figure 1 & 2)
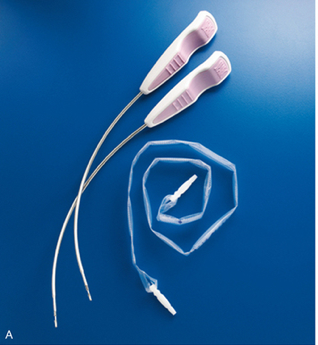
Figure 1: Sparc TVT sling device
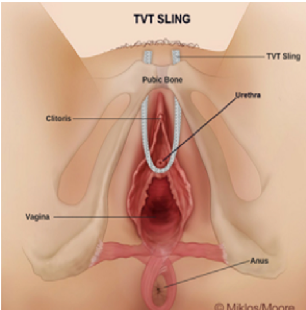
Figure 2: Sparc TVT sling
She complains that she lives with pain, which she describes as a (7/10) but her pain is made worse with intercourse (10/10). Pain is aggravated by physical activity, household chores as well as sex. She complains of pain in the pubic area i.e. the lower abdomen as well as in the vagina. Looking at the location of the Sparc TVT mesh sling in the human body it is easy to see that her pain is along the pathway of the TVT mesh sling. (Figure 2)
After urodynamic testing and appropriate evaluation and exam, Dr. Miklos confirmed that the sling was indeed responsible for both her vaginal and suprapubic pain. He recommended she have the complete sling removed and replaced with an older “gold standard” anti-incontinence surgical procedure known as a Burch procedure. After informing the patient of the risks, benefits, complications as well as alternatives to the recommended surgery the patient agreed to:
- Removal of the vaginal portion of the TVT sling
- Removal of the arms of the TVT sling (Figure 3) causing pain in her lower abdominal and pubic area
- Replacing the sling with a NON-MESH procedure known as the laparoscopic Burch procedure. (Figure 4)
The patient had her whole TVT mesh sling removed and simultaneously replaced with a non-mesh incontinence procedure known as a laparoscopic Burch.
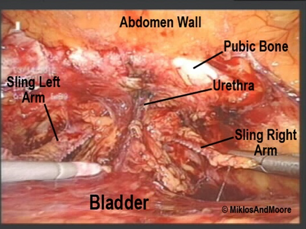
Figure 3: TVT sling laparoscopic dissection
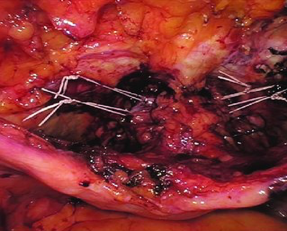
Figure 4: Burch sutures replace the TVT
The patient surgery was performed without complication and a blood loss of less than 25 mL or one tablespoon. Her pain continues to improve and she no longer has stress urinary incontinence.